Ionic Liquid

What is an Ionic Liquid?
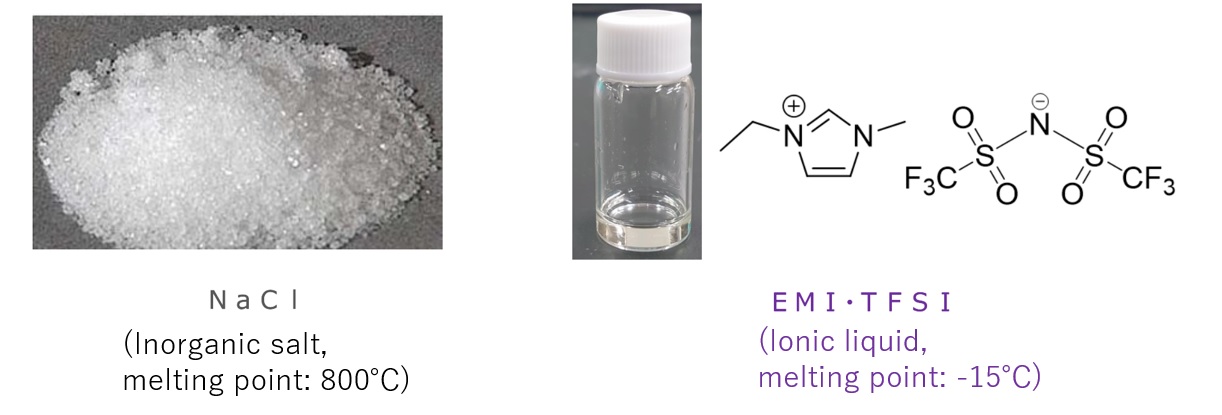
A salt (a compound consisting of a cation and an anion) that has a low melting point and is a liquid near room temperature.
Comparison of Appearance of Inorganic Salts and Ionic Liquids

Main Features of Ionic Liquids
1
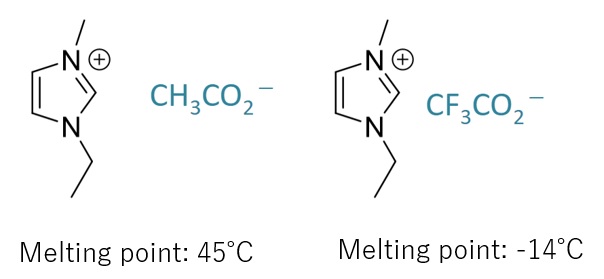
Low Melting Point
Ionic compounds generally have a high melting point, while ionic liquids have a low melting point due to their structure that weakens interactions and inhibits crystallinity.
(The melting point can be controlled by molecular design and combination of anions and cations.)
Lower electron density of ionic groups due to electron-withdrawing groups, etc., results in a lower melting point
2
Low Volatility
The vapor pressure is very low due to the presence of electrical interactions between ions. There is little concern about air pollution or ignition due to volatilization.
Difference between organic solvents and ionic liquids
| Organic solvent | Ionic liquid |
|---|---|
| Volatile Air pollution and ignition concerns | Low volatility Less concern about air pollution and ignition |
Vapor pressure of each liquid
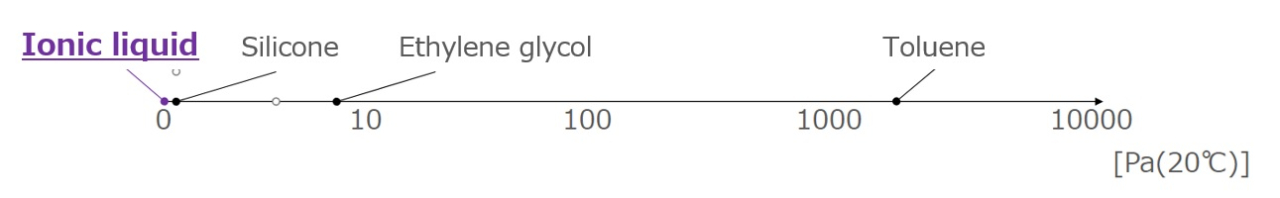
3
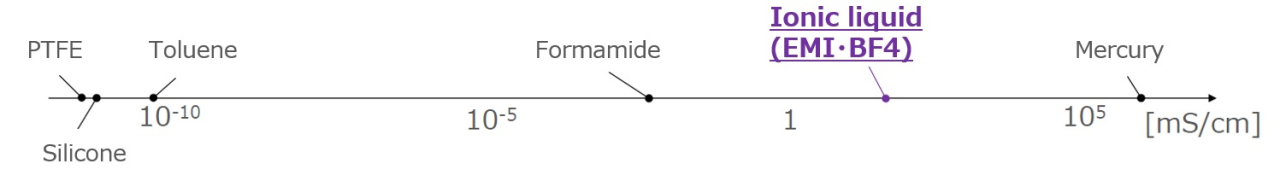
High Ionic Concentration and High Conductivity
Since it is composed solely of ions, it has a high ionic concentration and high electrical conductivity.
Electrical conductivity of each liquid
Examples of Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids
Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids Part 1: Electrolyte for Capacitors
Why Ionic Liquids are Used as Electrolyte for Capacitors?
- Low melting point: No precipitation even at low temperatures
- High conductivity: High conductivity can be achieved by increasing the concentration of electrolyte
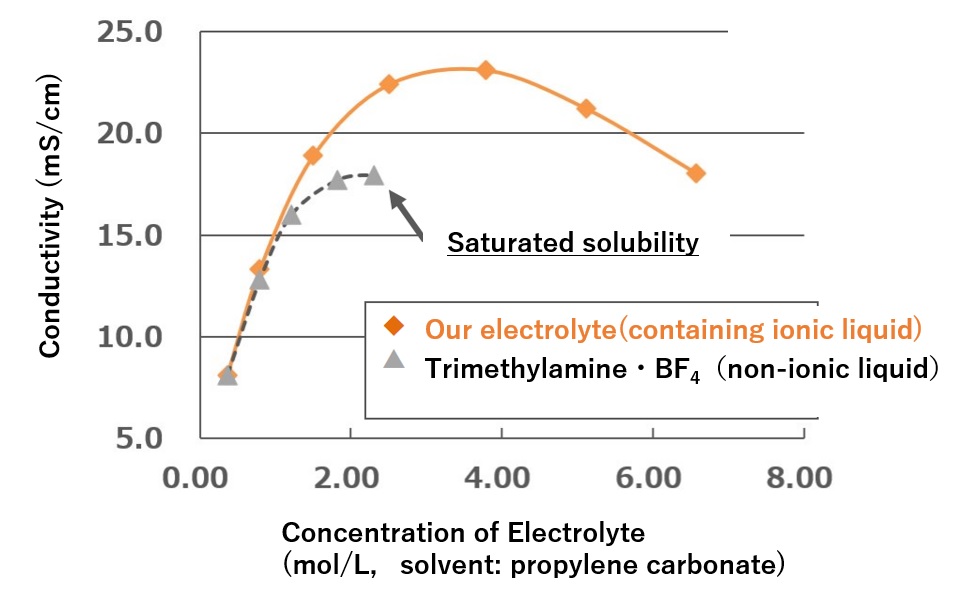
Conductivity and Low Temperature Solubility Data for Ionic Liquids and General Amine Salts
| Our electrolyte (Ionic liquid) |
Triethylamine phthalate (Non-ionic liquid) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity mS/cm(@30℃) | 14.2 | 6.0 |
| Low temperature solubility( -55℃) | Good (Dissolution) | Poor (precipitation) |
High Conductivity by Ionic Liquids
Antistatic Agent - Fluorine-free ionic liquid product developed by our company
Our developed product uses a composition that does not contain fluorine elements and has low corrosiveness.
In addition, its large molecular size makes it difficult to bleed out.
Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids Part 2: CO2 Gas Absorbent
Why Ionic Liquids are Used
- Low volatility: Low loss in process
- Design freedom: Can be selectively structured to easily adsorb CO2
(1)Adsorption in crevices due to its bulky structure (physical adsorption)
(2)Reacts with CO2(chemisorption)
This page has been prepared solely for information purposes.
Sanyo Chemical Industries, Ltd. extends no warranties and makes no representations as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained herein, and assumes no responsibility regarding the suitability of this information for any intended purposes or for any consequences of using this information.
Any product information in this brochure is without obligation and commitment, and is subject to change at any time without prior notice.
Consequently anyone acting on information contained in this brochure does so entirely at his/her own risk.In particular, final determination of suitability of any material described in this brochure, including patent liability for intended applications, is the sole responsibility of the user. Such materials may present unknown health hazards and should be used with caution. Although certain hazards may be described in this brochure, Sanyo Chemical Industries, Ltd. cannot guarantee that these are the only hazards that exist





