Wax Basics
Definition and Classification of Wax
Wax is a generic term for a wax-like substance, which is defined as "(1) solid or semi-solid at room temperature, with a melting point of 40°C or higher, and (2) melting without decomposition when heated and of low viscosity.
Waxes are composed of various raw materials and can be broadly classified into natural waxes, semi-synthetic waxes, and synthetic waxes.
Features and Classification of Synthetic Waxes
Waxes have a wide range of applications and are used as raw materials or additives for many industrial products and daily necessities such as cosmetics, printing inks, tires, flooring, and adhesives.
Synthetic waxes are widely used as industrial raw materials for paints, inks, adhesives, etc., because they are relatively easy to control in terms of composition, melt viscosity, and other properties, and can meet a wide variety of needs.
Synthetic waxes can be classified into a polymerization type or pyrolysis type based on the manufacturing method. Polymerization type includes monopolymerization of ethylene monomers and modified low molecular weight polyethylene copolymerized with ethylene and other polar monomers. The pyrolysis type is a low molecular weight product made by radical decomposition of high molecular weight polyethylene resin or polypropylene resin.
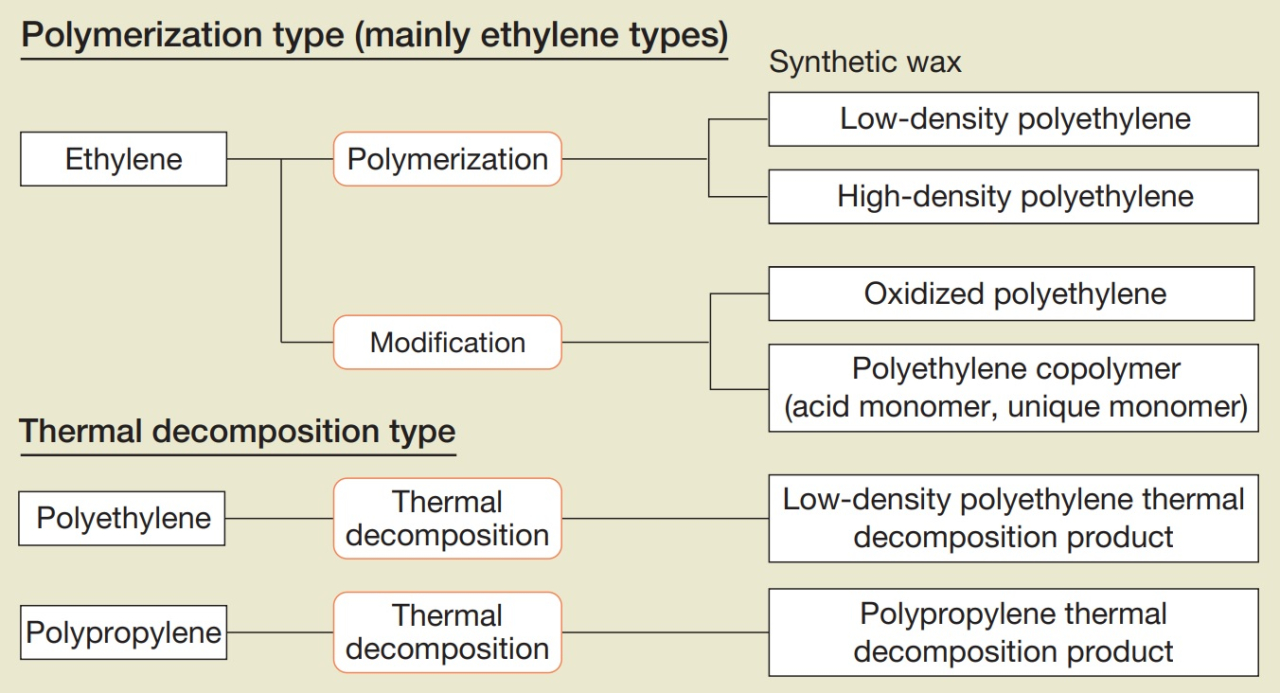
Characteristics of Synthetic Waxes
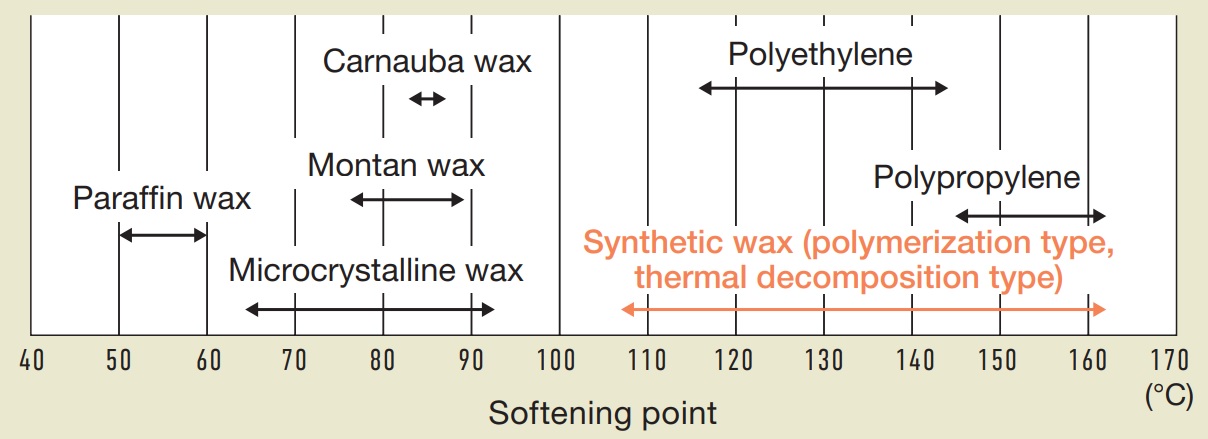
Structural Characteristics of Polymerized and Pyrolytic Waxes
| Manufacturing method | Pyrolysis type (our product) | Polymerization type (high pressure) | Polymerization type (low pressure) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight distribution Mw/Mn | Broad | Narrow | Broad |
| Spatial structure | Contains long-chain branching | Contains short-chain branching (usually methyl group) | Contains long-chain branching |
Our Main Lineup of Polyethylene and Polypropylene Waxes
We manufacture and sell the low molecular weight polyethylene "SANWAX" series, which was the first synthetic wax to be successfully industrialized in Japan, and the low molecular weight polypropylene "VISCOL" series, to which we applied this technology.
Features of the SANWAX and VISCOL
- High softening point and high crystallinity compared to natural waxes.
- Excellent compatibility with polyolefin resins.
- Wide molecular weight distribution due to the thermal decomposition process.
- Easily compatible with resins other than polyolefins.
The industrial process of pyrolysis is also more suitable for small-lot production in comparison to polymerization-type industrial process, and can be finely tailored to various needs.
Main Lineup of Polyethylene Wax "SANWAX" Products
| SANWAX 161‐P | SANWAX 131-P | SANWAX 151-P | SANWAX 171-P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | High molecular weight | Medium to high molecular weight | Small to low molecular weight | Low molecular weight |
| Appearance | White powder | White powder | White powder | White powder |
| APHA color | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Melting point (℃) | 103 | 102 | 101 | 100 |
| Melt viscosity (mPa・s) | 4300 | 1000 | 290 | 180 |
| Molecular weigh (Mw) | 27000 | 20000 | 13000 | 10000 |
| Main applications | Pigment dispersants, filler dispersants, flow improvers | |||
Test Method
APHA color : Hasen method, Melting point: DSC method, Melt viscosity: 140°C, Molecular weight: High temperature GPC method
Main Lineup of Polypropylene Wax "VISCOL" Products
| VISCOL 330‐P | VISCOL 440-P | VISCOL 550-P | VISCOL 660-P | VISCOL LM-500 (Development product) | VISCOL LM-600 (Development product) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | High molecular weight | Medium to high molecular weight | Small to low molecular weight | Low molecular weight |
|
|
| Appearance | White powder | White powder | White powder | White powder | Light yellow powder | Light yellow powder |
| APHA color | 200 | 200 | 200 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Melting point(℃) | 145 | 144 | 139 | 136 | 125 | 119 |
| Melt viscosity (mPa・s) | 4000 | 1800 | 200 | 70 | 1400 | 100 |
| Molecular weight (Mw) | 40000 | 27000 | 13000 | 10000 | 30000 | 9000 |
| Main application | Pigment dispersants, filler dispersants, flow improvers | |||||
Test Method
Color number: Hazen method (*Gardner method), melting point: DSC method, melt viscosity: 160°C (*140°C), molecular weight: high temperature GPC method





