Plastics Molding Basics
Thermoplastic Molding Methods
- Extrusion molding
- Injection molding
- Blow molding
1. Extrusion molding
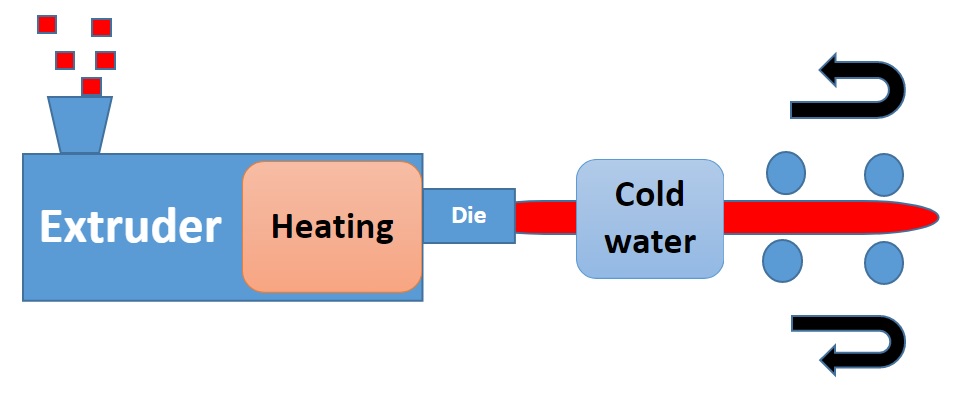
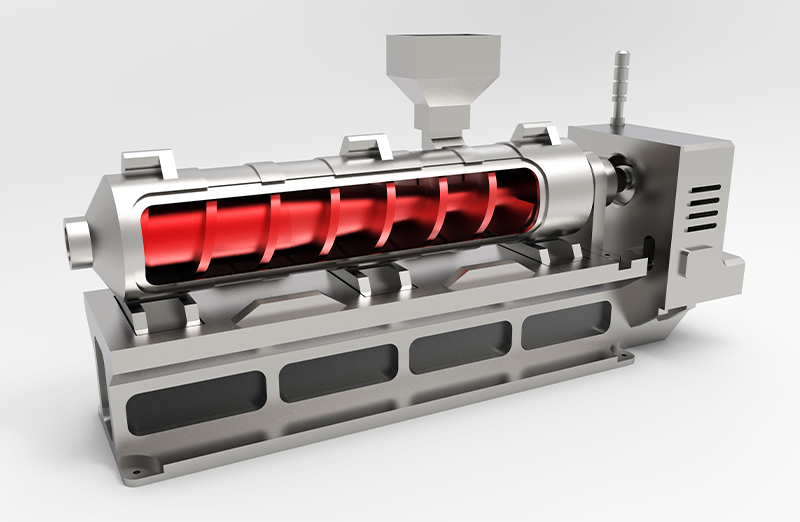
In extrusion molding, molten resin is extruded through an extrusion port called a die or dies by a screw in an extruder cylinder and cooled in air or moisture as it solidifies. This method is suitable for continuously forming molded products with an unchanging cross-sectional shape. It is broadly classified into pipe molding, sheet molding, film molding, and filament molding, and film molding is further classified into T-die molding, inflation molding, laminate molding, and stretched film.
Extrusion molding is similar to injection molding since the resin is extruded by a screw, but the difference is that in injection molding, the resin is injected into the mold and shaped, whereas in extrusion molding, the resin is shaped by the shape of the extrusion opening.
2. Injection molding
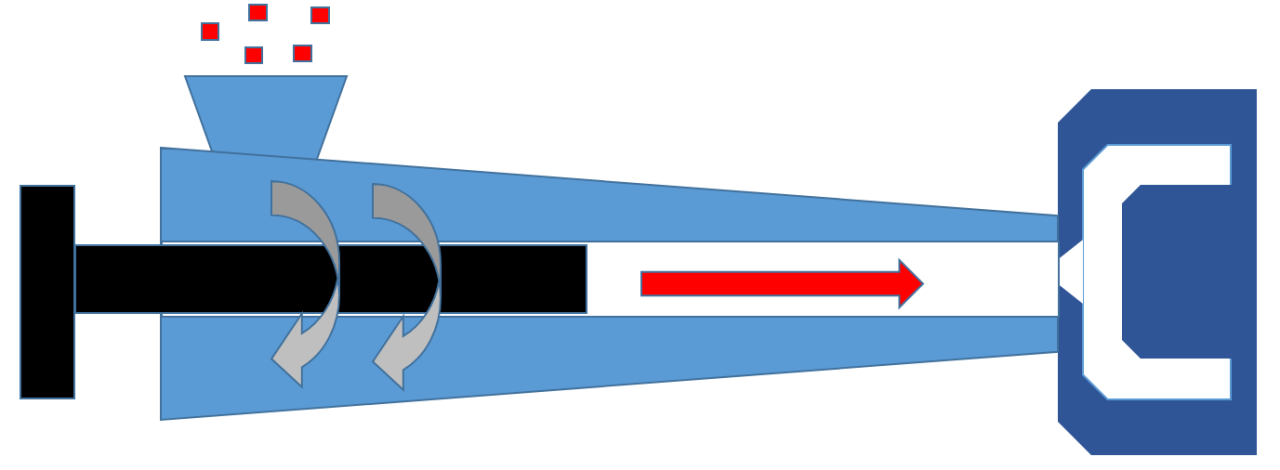
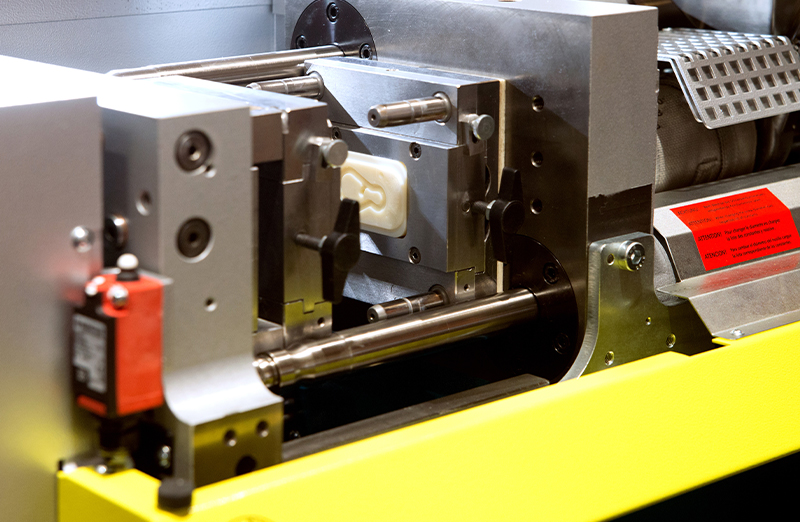
This is a molding method in which molten resin is injected into a mold by a screw in an extruder cylinder.
- A molding method that produces three-dimensional shaped molded products such as buckets and bottles.
- Materials are heated to melt, fed into a mold, and then cooled to create a molded product.
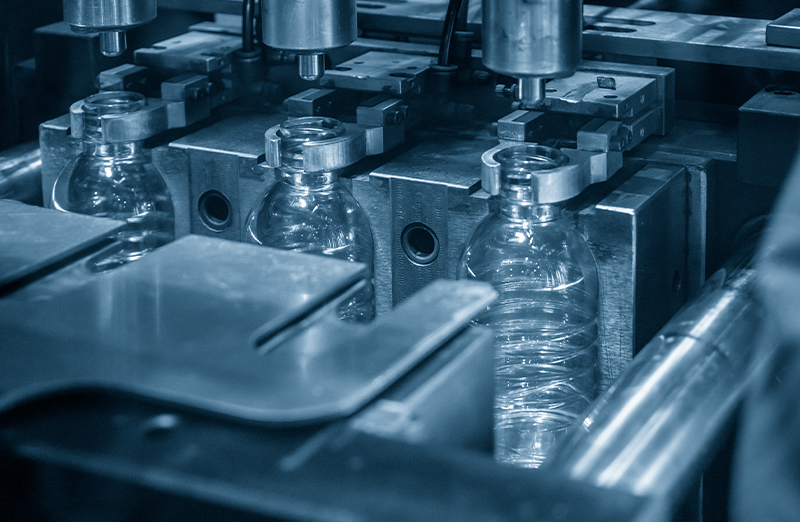
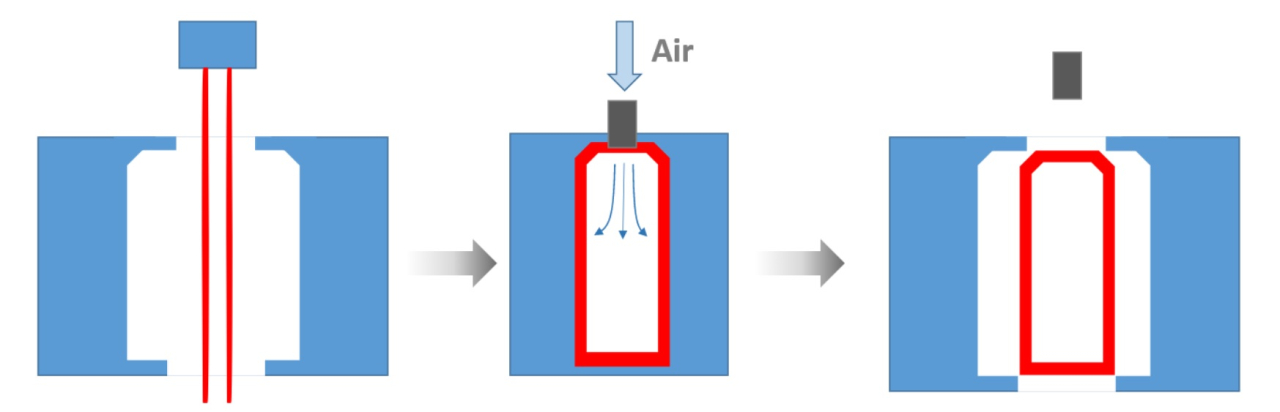
3. Blow Molding
- Blow molding is a molding process in which thermally melted resin is extruded into a pipe shape, compressed air is blown in while the resin is soft, and the resin is pressed against the mold to cool and solidify.
- Molding method for making hollow molded products with small openings, such as shampoo containers, even with three-dimensional shapes.

What is a lubricant?
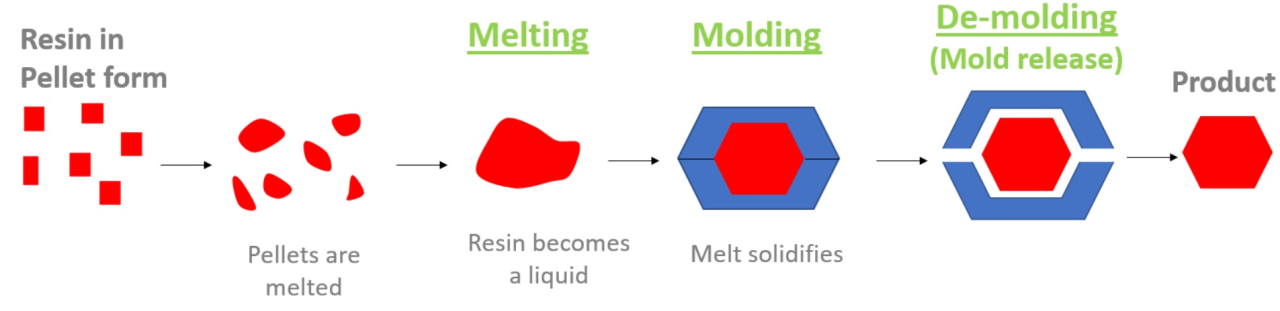
Lubricants are agents added to thermoplastic resins during heat molding to improve their fluidity for easier processing and to make it easier to remove molded products from the mold.
They are additives that play an active role in the melting, molding, and demolding processes.
Lubricants are agents added to thermoplastic resins during heat molding to improve their fluidity and facilitate processing and to make it easier to remove molded products from the mold (mold release). (Ref: Dictionary of Chemistry)
Molding Process and Mold Release Issues
Major Causes of Poor Resin Flow During Molding Process
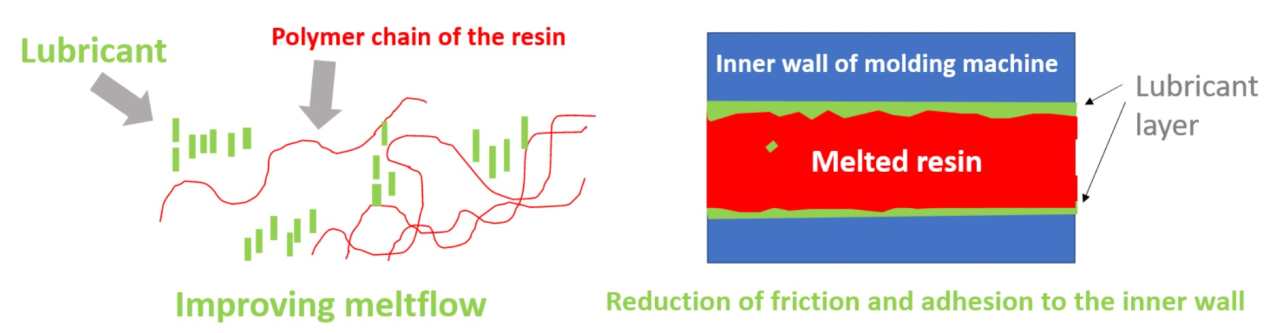
- Frictional resistance between the molten resin liquid and the inner wall of the molding machine is high.
- The resin melt itself is highly viscous and difficult to flow.
- At the beginning of melting, the frictional resistance between the resins becomes large and the viscosity increases rapidly.
The Main Cause of Poor Mold Release...
After processing, the resin adheres to the inner walls of the molding machine.
Effect of Lubricant (Low Molecular Polyolefin)
- Improved flowability of resin melt.
- Prevent viscosity increase of resin pellets at the beginning stage of melting. Reduce the viscosity of polyolefin resin during molding.
- When molds are used, the adhesive force between the hardened resin and the mold is reduced. (Aacceleration of mold release)
Reference Data
- My First Plastic Isao Sato
- Introduction to Polymeric Agents, supervised by Takehiko Fujimoto, Sanyo Chemical Co.
- Performance Chemicals Function Series No. 7 (Flexible and Plastic Functions)
- Performance Chemicals Function Series No. 8 (Thickening and Thinning Functions)
Related Products, Topics
Lubricants: Click here for the VISCOL and SANWAX product introduction page






