Antistatic Agents Basics
Permanent antistatic agent introduction video
Mechanism of Static Electricity Generation
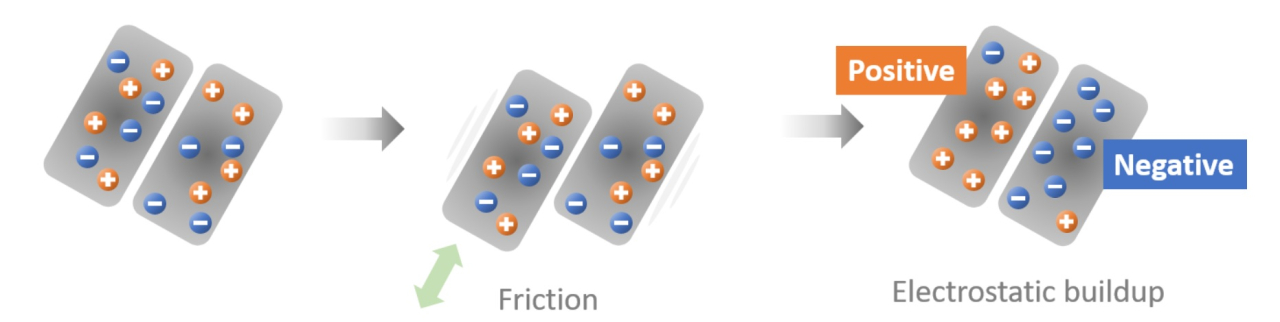
Charging refers to the phenomenon of an object becoming electrically charged, and electricity that is charged and remains motionless is called static electricity.
The mechanism by which static electricity is generated is that when objects are rubbed against each other, electrons move between the objects, causing a positive and negative imbalance, and in the case of insulators such as plastic, the generated electricity cannot escape, resulting in the generation of a charge.
Positively charged and negatively charged
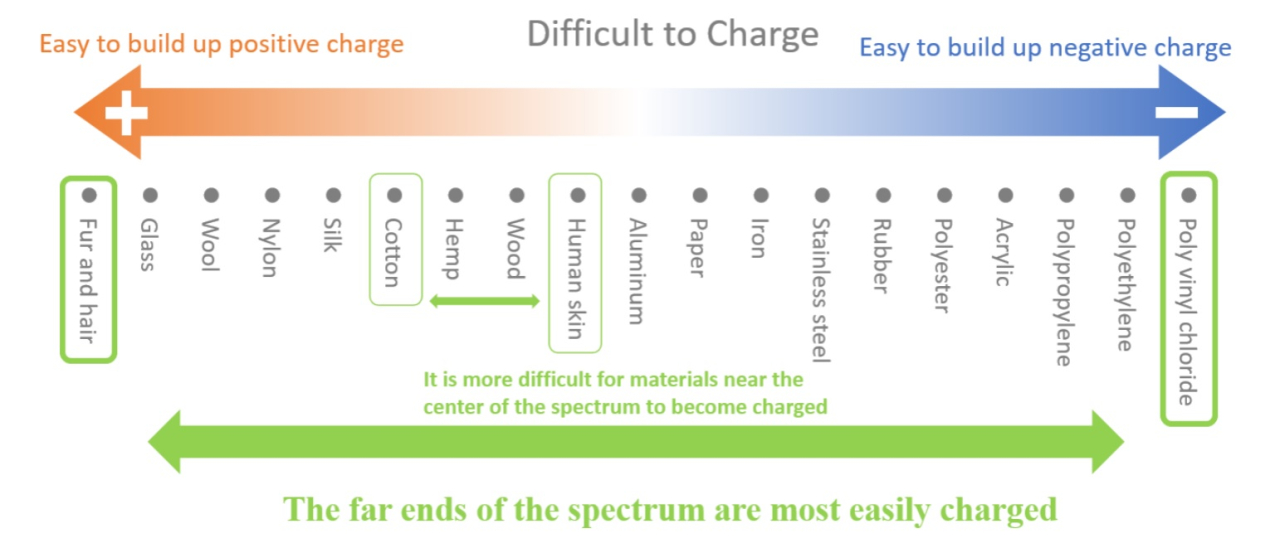
Some substances are positively charged and some are negatively charged.
The order in which they are positively and negatively charged is called the charging sequence.
When two materials are rubbed together, if they are close to each other in the charging sequence, such as human skin and cotton, static electricity will not be generated, but if they are far from each other in the charging sequence, such as polyvinyl chloride and hair, static electricity will easily be generated.
Some of you may have rubbed a carpet pad against your head to generate static electricity when you were young. Many underlays are made of polyvinyl chloride, and the combination of the underlay and hair is extremely susceptible to static electricity.
Triboelectric series
Why is Antistatic Needed?
There are three reasons why antistatic is necessary.
- Prevention of Dust Adhesion
When you try to wipe off dirt, static electricity may cause dust to stick to the surface. - Prevents electronic components from malfunctioning and short-circuiting
Electrostatic disturbances occur in the manufacturing process of semiconductors and other products.
- Explosion-Proof Compliance
Explosion-proof compliance is mandatory for chemical plants, etc., and must be addressed.
Plastic is an insulator, so it is easily electrically charged and dust adheres to the surface.

Antistatic Agent Addition Test to Prevent Dust Adhesion to Film
The figure below shows a comparison of films with and without antistatic agent added during film molding.
The left image shows static electricity generation and dust adhesion, while the right film with added antistatic agent shows no dust adhesion.
Dust and other contaminants are prevented from adhering to the film during production.

Examples of Plastic Products Where Static Electricity is Not Desirable (1)
Prevention of Powder and Dust Adhesion
This shows applications where antistatic agents play an active role.
They are used in films for electronic packaging materials, transparent dust boxes for cyclone vacuum cleaners, air conditioners, and medical applications such as powder aspirators and protective clothing.

Films
(e.g., electronic packaging materials)

Inhaler
(powder aspirator)

Transparent container
(e.g., cyclone vacuum cleaner dust box)

Electrical appliances
(e.g., air conditioners)
Plastic Products Where Charging is Not Desirable (2)
Explosion-Proof Compliance, Protection of Electronic Components
Other applications include explosion-proof helmets and flashlights, trays for electronic components, flexible containers for powders, and protective films.

Explosion-proof products
(e.g., helmets)
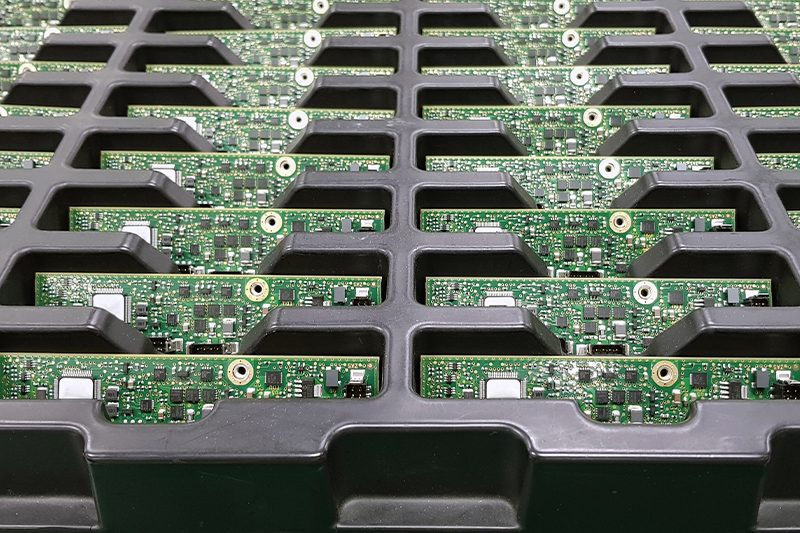

Trays for electronic components (e.g. IC chip trays)
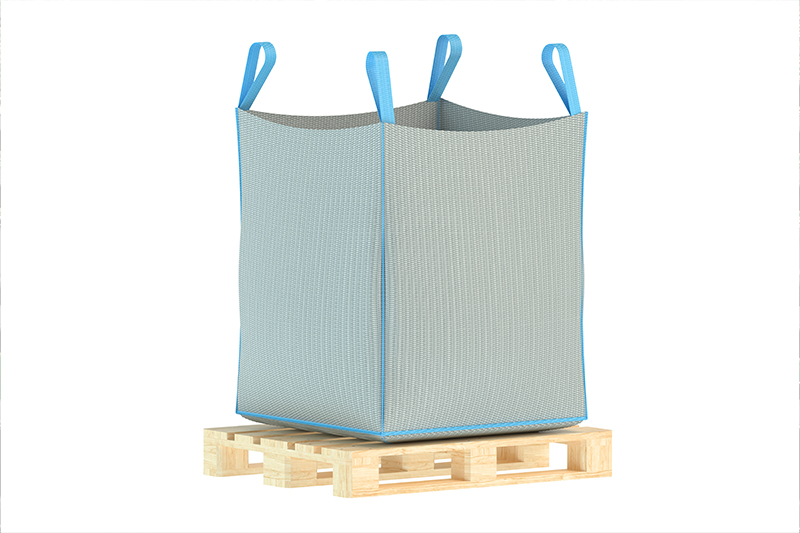

Flexible Container
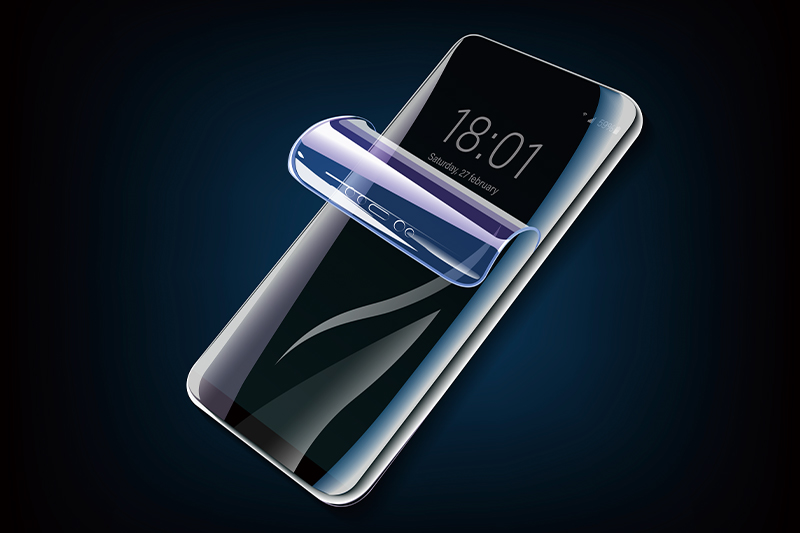

Protective film
(e.g. LCD protective film)
Antistatic ・・・・ How can we help?
The reason static charge occurs is because friction occurs and static electricity does not escape.
Plastics easily generate static electricity, so antistatic measures can be taken by allowing the generated electricity to escape.
Strategies to release electricity by preventing charging
Ionic Conduction
Add an ionic substance and use moisture + ions to carry and release electricity.
Electron Conduction
Add a compound that conducts electricity well (conductor) to create a path for electricity to escape.
The purpose of antistatic of plastics and the target surface resistivity
The index of static charge is expressed in terms of surface resistivity. A high surface resistivity value causes charging.
Since the targeted level of surface resistivity differs depending on the purpose, it is necessary to adjust the type and amount of antistatic agent added according to the purpose.
The table below summarizes the antistatic phenomena, antistatic purposes, and applications for each surface resistivity value.
| Surface resistivity (Ω/sq.) | Electrification | Antistatic purpose | Application examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| >1013 | Static electricity builds up | (Insulation) | (Insulating material) |
| 1012 〜 1013 | Charged but slowly dissipates | Preventions dust and dirt adhesion | Vacuum cleaner dust box |
| 1010 〜 1012 | Charged but quickly dissipates | Protection from sparks/explosions | Explosion-proof helmet |
| < 1010 | Non-charged | Protection of electronic components and circuits | Trays for electronic components |
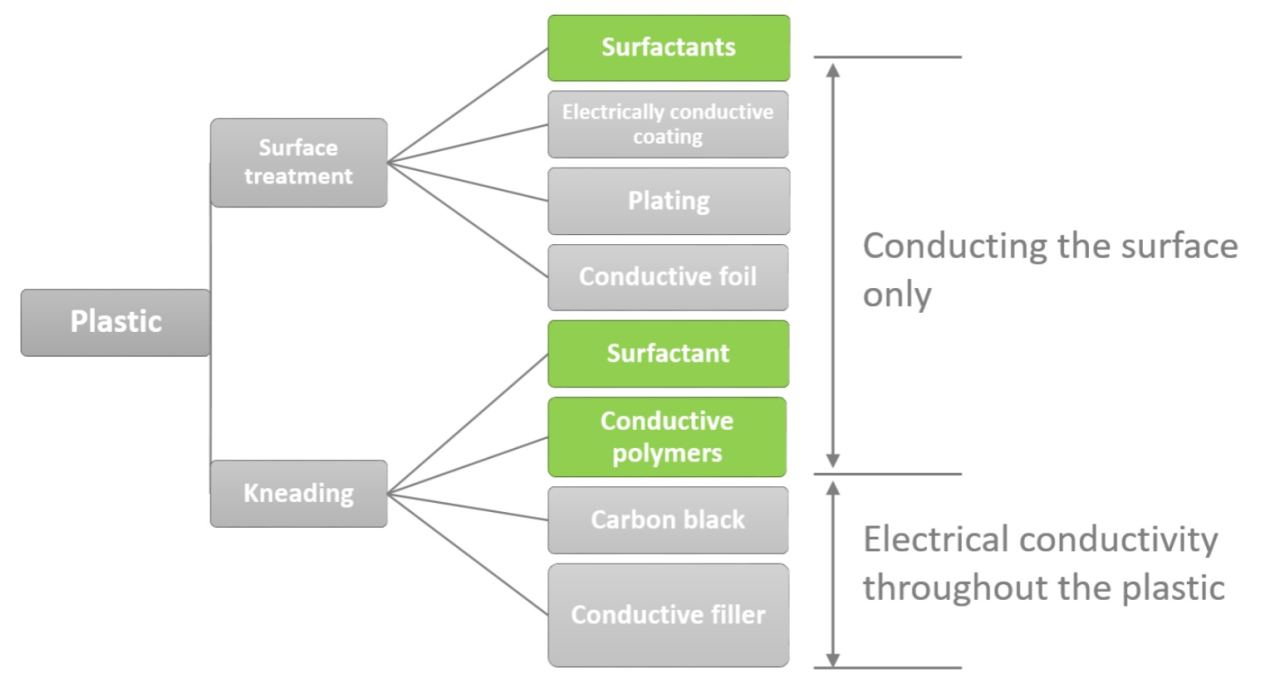
Classification of Antistatic Agents
Antistatic agents can be classified into those that conduct electricity on the surface of plastics and those that conduct electricity within the plastics themselves.
Surfactants and conductive paints are applied, or conductive polymers or carbon black are kneaded into plastics.
1) Surfactant-type Antistatic Agent
(Our Product "CHEMISTAT", "SANSTAT")
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Drawbacks |
|
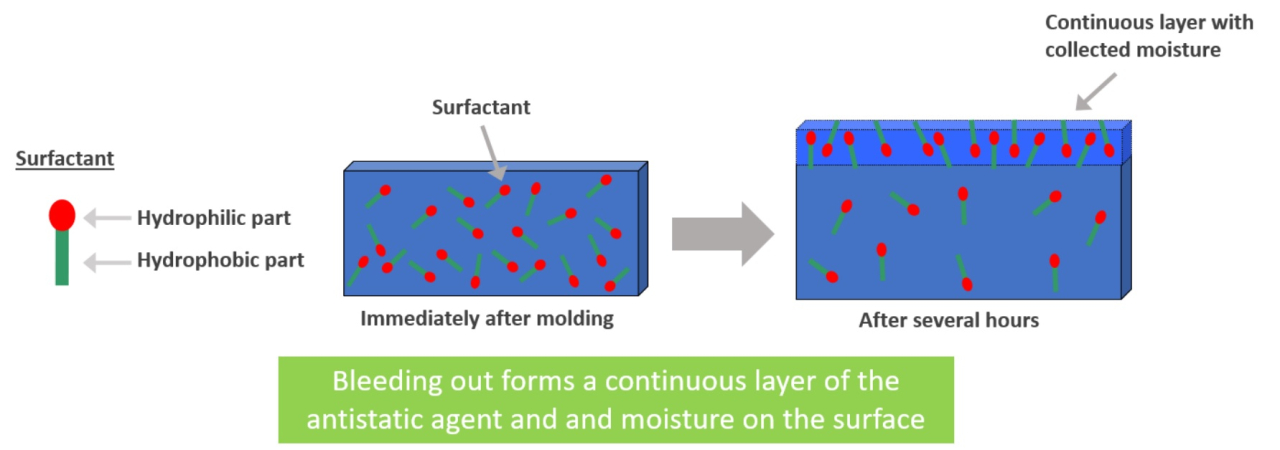
2)Conductive Filler/Carbon Black (None of Our Products)
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Drawbacks |
|
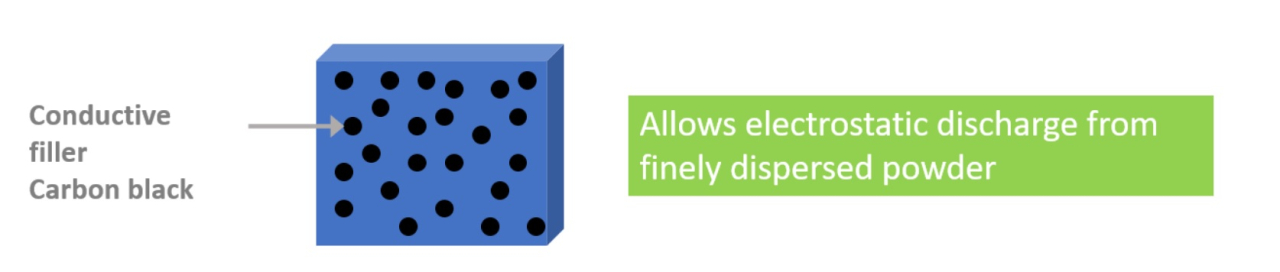
3)Conductive Polymers
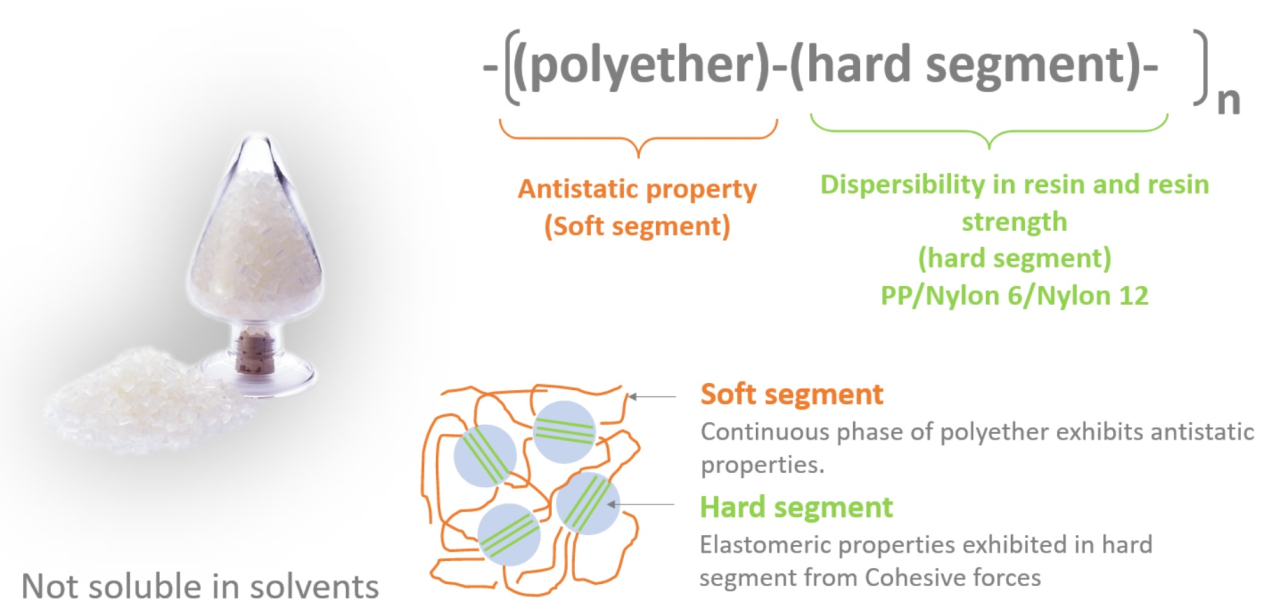
(Our Product: Permanent Antistatic Agent "PELESTAT", "PELECTRON")
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Drawback |
|

If you are looking for an antistatic agent, give us a call!
Reference Data
- Performance Chemicals Functional Series No. 10 (Prevents Electrification)
- Sanyo Chemical News No.518 (Performance Chemicals)
Related Information and Topics
Related Products
- Surfactant-type Antistatic Agents
Technology Topics